How to Upload Code to Github and Share Eclipse
This tutorial describes the usage of the Eclipse IDE to perform Git operations.
1. Git support for Eclipse
Via the Eclipse IDE you lot tin can perform Git commands like staging, commit, merge, rebase, pull and push.
2. Installation of Git back up into Eclipse
Most Eclipse IDE distributions from Eclipse.org already incorporate back up for Git. In this case no additional installation is required.
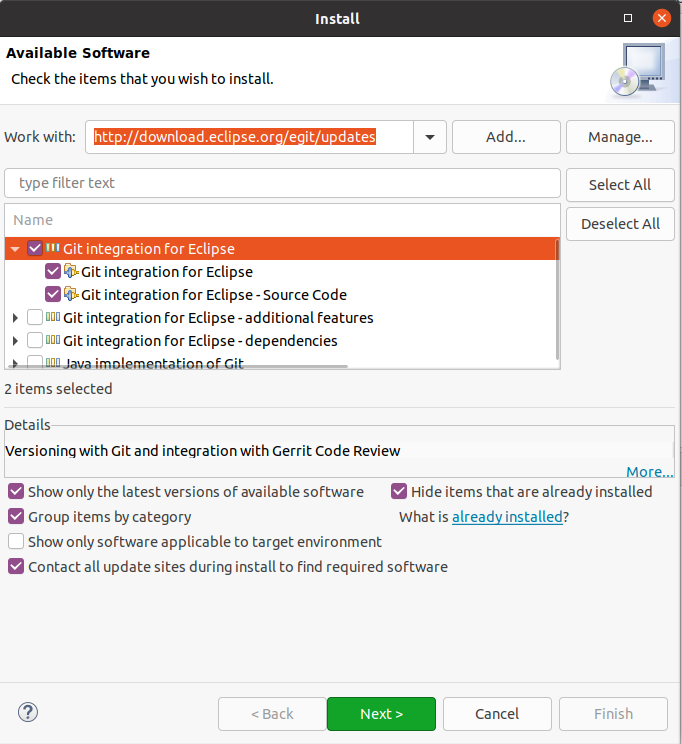
If the Git tooling is not available, you can install information technology via the Eclipse installation managing director. Select the carte entry. Enter 1 of the following update site URLs:
# Use this update site to get the latest release http://download.eclipse.org/egit/updates # utilize this update site to get the nighttime build http://download.eclipse.org/egit/updates-nightly/ The dialog to install the Eclipse Git squad provider is depicted in the following screenshot.
three. Configuration for Git usage via the Eclipse IDE
| Interoperability of Git command line settings with the Eclipse IDE If you lot take already configured Git for the control line, no additional setup is required in the Eclipse IDE and y'all can skip this exercise. The Eclipse IDE uses the same configuration files as the Git command line tools. This makes information technology easier to employ the Eclipse Git tooling and the command line tooling for Git interchangeable. |
3.i. Configure user and email
In your Eclipse IDE, select the entry. Configure your total proper noun and email in the user settings. As the Eclipse IDE uses the aforementioned settings every bit the Git command line, this might already exist done.
For the user the user.proper noun key is used, for the email the user.email central is used.
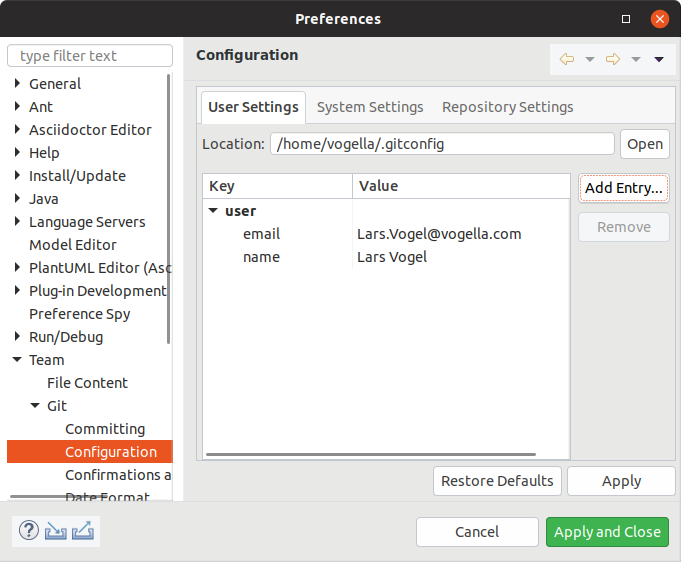
If these keys are not available press the Add Entry… push button and add together them.
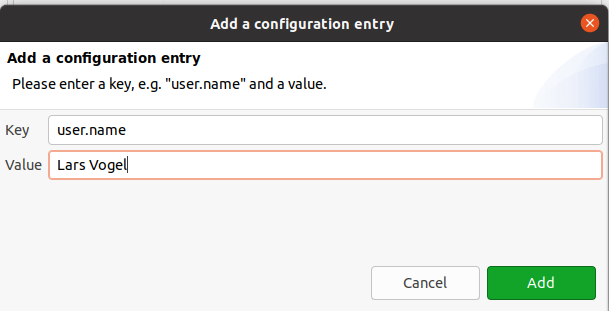
Echo the process for your email address via the user.email cardinal.
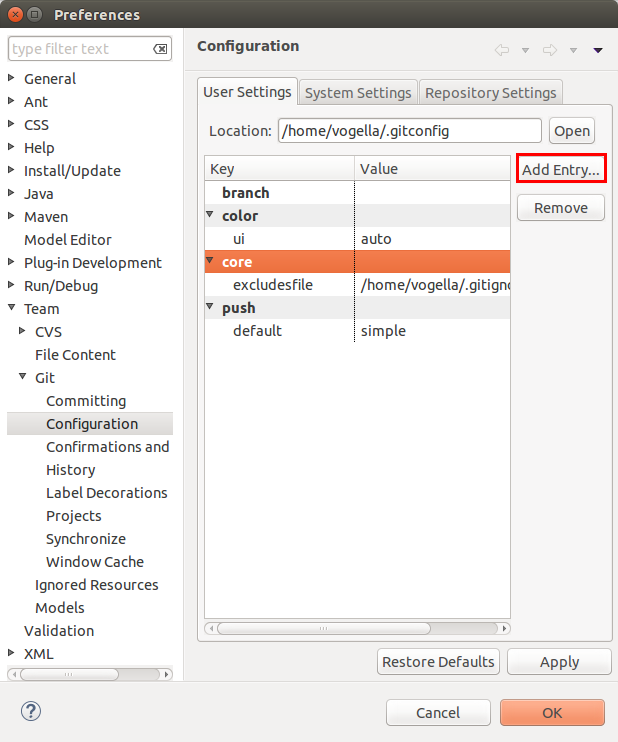
iii.2. Configure Git to rebase during pull operations
To use rebase during the pull operation set the pull.rebase parameter to true. Information technology avoids merge commits if you pull from a remote repository and accept divergent changes and instead rebases your local branch on the remote branch information technology tracks.
This is recommended setting past the author of this text.
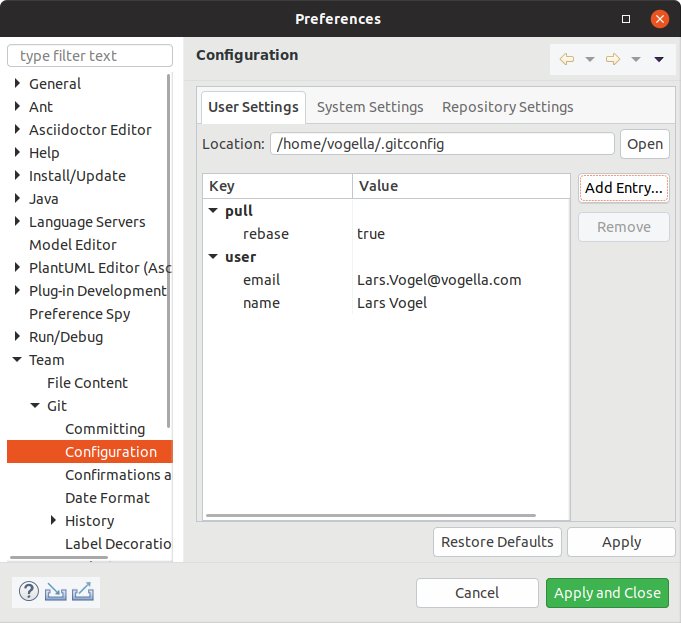
3.3. Validate the setup
After this setup, the configuration should look similar to the following screenshot.
three.4. Configuring the proxy settings
If yous are using a proxy server, you lot tin can configure it via .
4. Practise: Working with Git repository in Eclipse
The following practice explains how to use the Eclipse IDE to perform Git operations. To ensure that you accept a Git repository, you first create a new local Git repository via the Eclipse IDE.
| The Eclipse workspace and Git repositories It is practiced do to place your Git repositories outside the Eclipse workspace. This separates your Git repository from whatever additional meta-data which Eclipse might create. By default, Eclipse Git uses the git folder in the users abode directory to clone new repositories. |
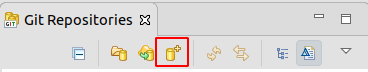
4.1. Create a new Git repository via Eclipse
Open the Git Repositories view via the menu entry. From the toolbar, select the Create a new Git repository and add it to this view entry.
This opens a dialog which allows you to specify the directory for the new Git repository. Select a new directory exterior of your workspace. By convention, this directory is a subdirectory in the git folder of the users dwelling house directory.
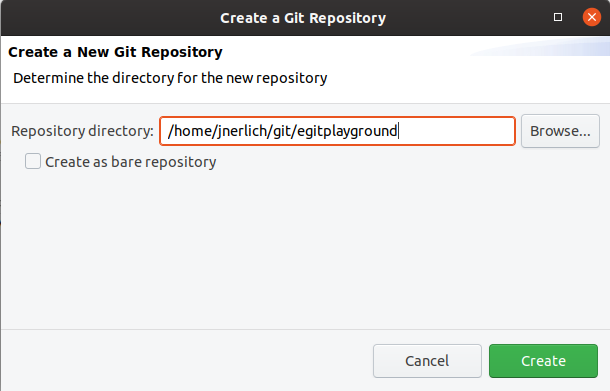
Press the Create push. Now the Git repository is created and a reference to it is added to the Git Repositories view.

4.ii. Create .gitignore file
We want to ignore certain file types in our Git repository. We desire Git to ignore the bin folder and *.class files.
Create a .gitignore file in the meridian-level folder of your Git repository. This ways, the file should be placed at the aforementioned level equally the .git directory.
Eclipse Git does non allow to create a file directly in the top-level folder of your repository. You take to practise this stride outside of the Eclipse IDE, either via the control line or via your system project explorer.
It should comprise the following content.
| Recent versions of MS Windows decided to foreclose you from renaming a file in the file explorer without using a file extension. Create a file in Notepad or Editor (new name for Notepad) and select Salvage-As. Ensure you have removed the .txt extension. |
4.3. Create a new project
Create a new Java project called com.vogella.git.kickoff via the menu entry.

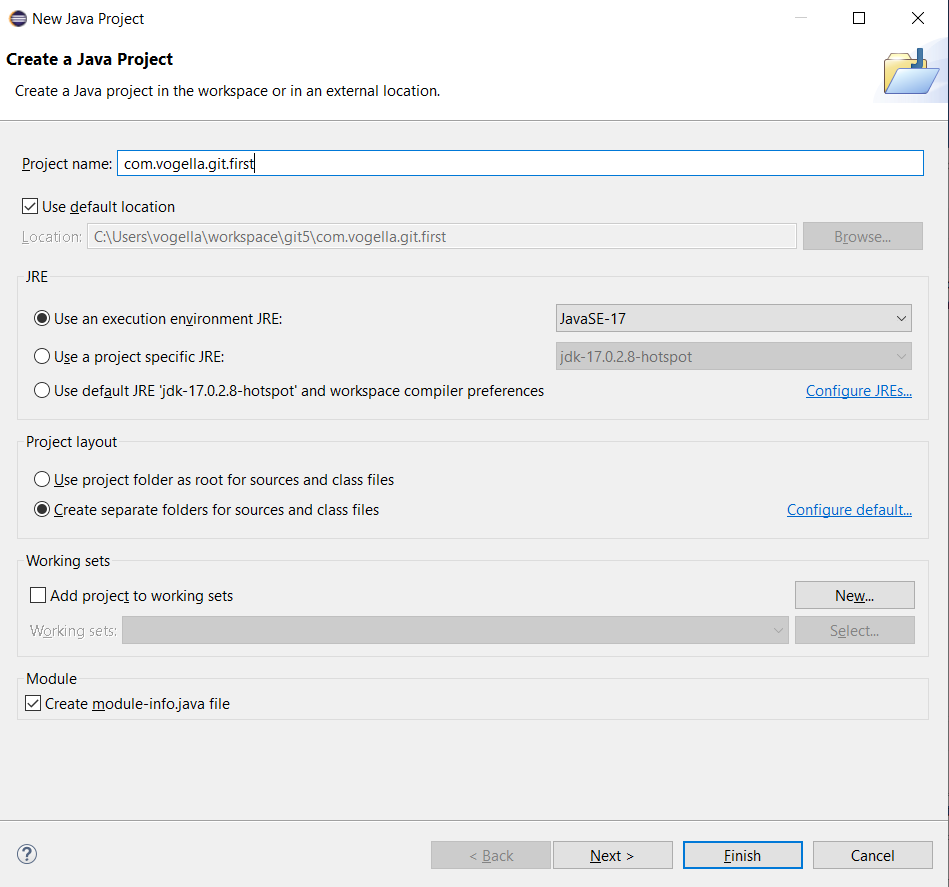
| If yous are using Java nine or higher, you volition be asked to create a module-info.java. The following dialog is not shown if you utilise Java viii or lower. |
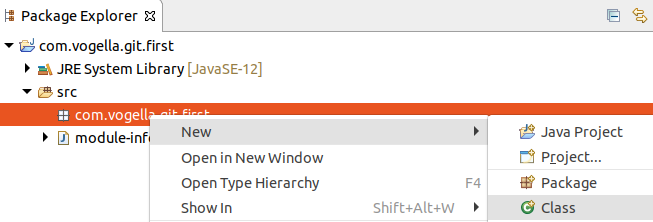
Right-click on the source folder and select and create the com.vogella.git.first parcel.
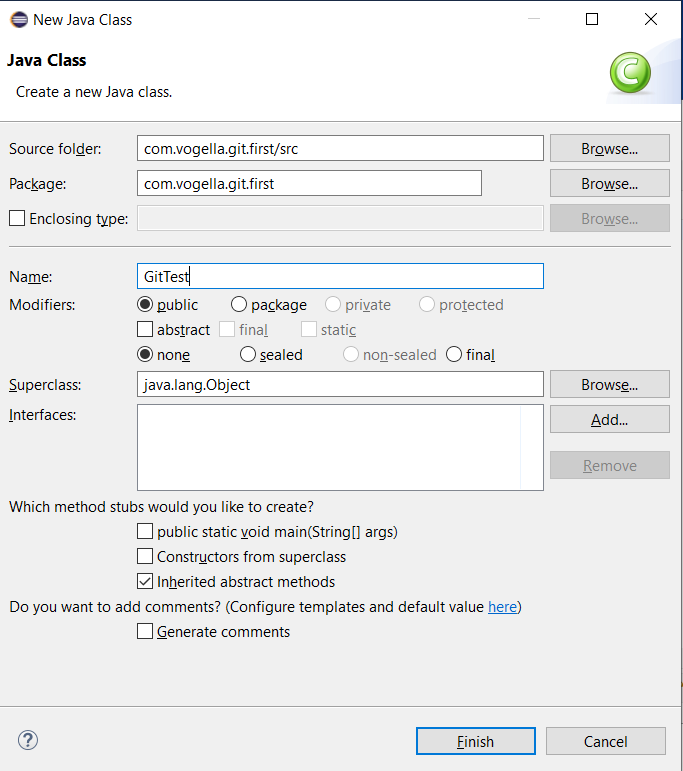
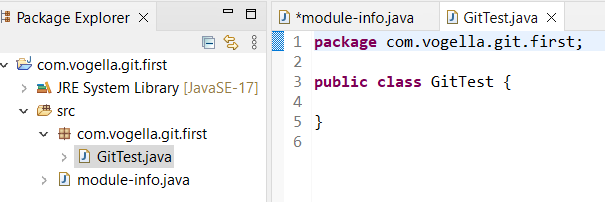
Correct-click on the package binder and select and create the following class.
package com.vogella.git.first ; public form GitTest { public static void main ( String [] args ) { System . out . println ( "Git is fun" ); } } 4.4. Put project under Git version control
To put your new project nether version command with Git, right-click on your project, select .
| If another version command system is installed you take to select that you lot desire to utilize Git as a version control system. |
Later, select your existing Git repository from the drop-downwards list and press the Finish button.
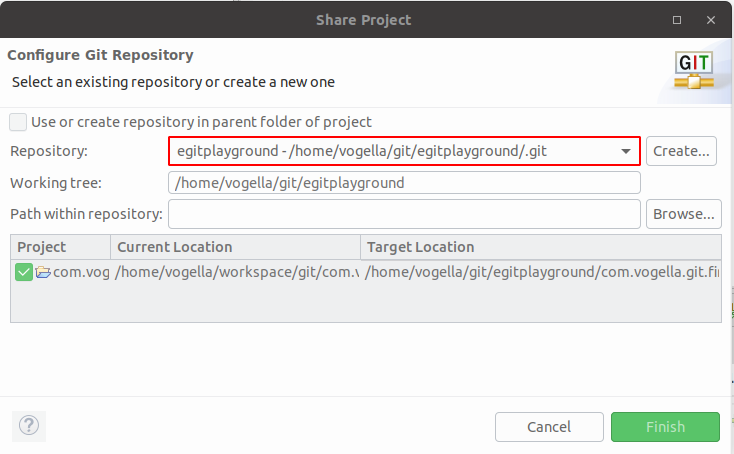
Press the Finish button. Your project is now moved to your Git repository.
The post-obit screenshot shows the directory in the Git Repository view. The .git directory contains the Git repository, the other directories contain the files of the working tree.

4.5. Using the Git Staging view for the initial commit
Open the Git Staging view, via . In this view drag all files into the Staged Changes area, write a meaningful commit message and printing the commit button.
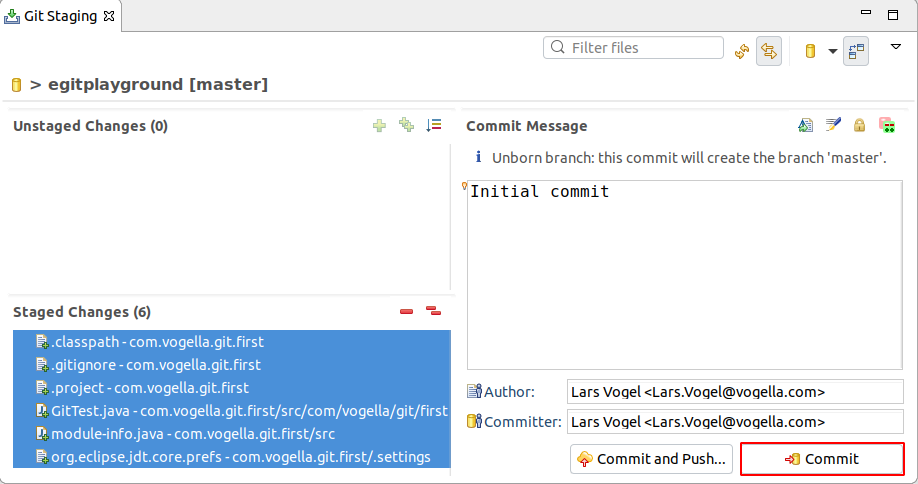
four.vi. Change a file and commit the change
Change the Organization.out.println message in your GitTest form.
bundle com.vogella.git.first ; public class GitTest { public static void main ( Cord [] args ) { Arrangement . out . println ( "Git is absurd" ); } } As well create a new file chosen Readme.adoc.
Commit the changes of the GitTest class simply exercise not add and commit the Readme.adoc file to the Git repository.
In the Git Staging view drag but the GitTest class into the Staged Changes area, write a meaningful commit message and press the commit push button.
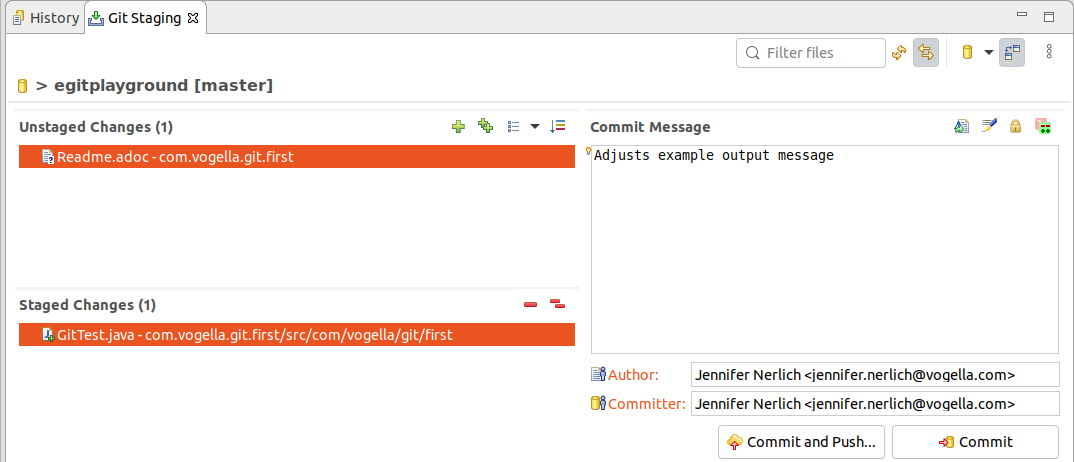
This change is now also stored in your local Git repository. The Readme.adoc file is neither staged nor committed to the Git repository.
4.7. Commit more than files
Commit the Readme.adoc file. By at present you lot should know that you have to stage the file and commit information technology.
4.viii. Configure the History view
Open the History view via the bill of fare entry.
In the History view click all toggle buttons every bit shown in the screenshot
-
Link with Editor and Choice
-
Show all changes in repository containing the selected resource
-
Show all Branches and Tags
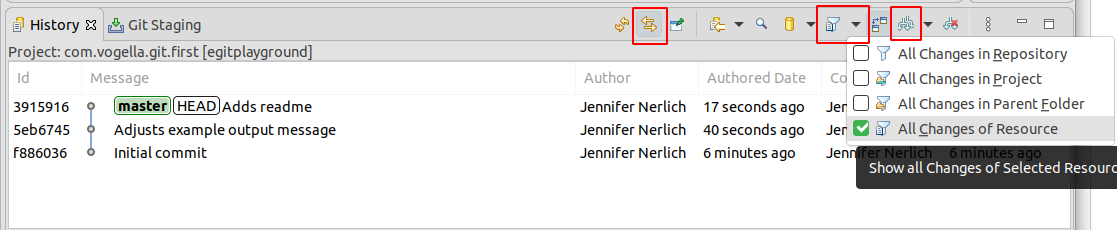
Later on, utilize the History view to review which files were included in your individual commits.
4.ix. Open up an older version with the current version of a file via the History view
We want to see the version of the GitTest.java file as information technology was in the first commit. Select the start commit in the history view, observe the file selected in the commit and select via the context carte.
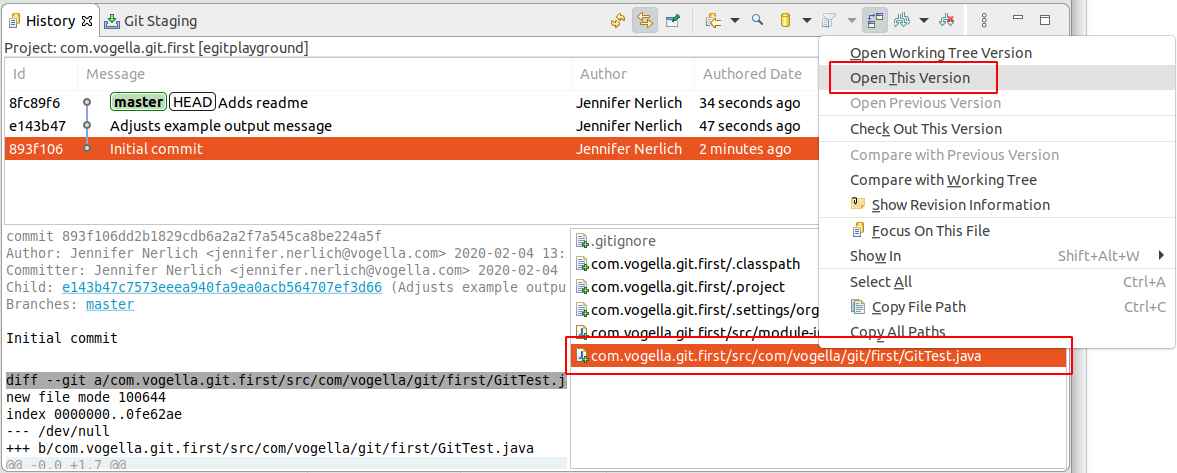
four.10. Accidently add a unwanted file an remove it
Create a new file nammed test.unwanted via right mouse click on your project and New → File from the context menu. Stage and commit the new file.
Now add *.unwanted it to your .gitignore file. Brand a change to your examination.unwanted file
Git shows it as change, equally changes in .gitignore only utilise to new files You demand to untrack the file.
Select the file and select Team → Untrack (or Team → Avant-garde → Untrack on latest Git support for Eclipse).
Stage and commit the alter.
iv.11. Add more projects to your Git repository
You can of course have multiple projects in a Git repository. To validate that, create two more Java projects called com.vogella.egit.multi.java1 and com.vogella.egit.multi.java2. Create at least one Java class in each projection.
Afterward select the new projects, right-click on them and select .
Select your Git repository in the post-obit dialog and add both projects to this repository. Printing the Finish push.
4.12. Validate the project movement and commit changes
Afterwards validate that the projects take been moved. You can checking your workspace directory and your Git repository directory via a file explorer. You see that the projects have been moved from there original location to the Git repository.
The changes have not yet been committed. Now commit all files in the two projects to your Git repository.
v. Practice: Clone an existing repository
In this exercise yous volition clone a Git repository and import the existing projects from this repository into your workspace.
For this, select .
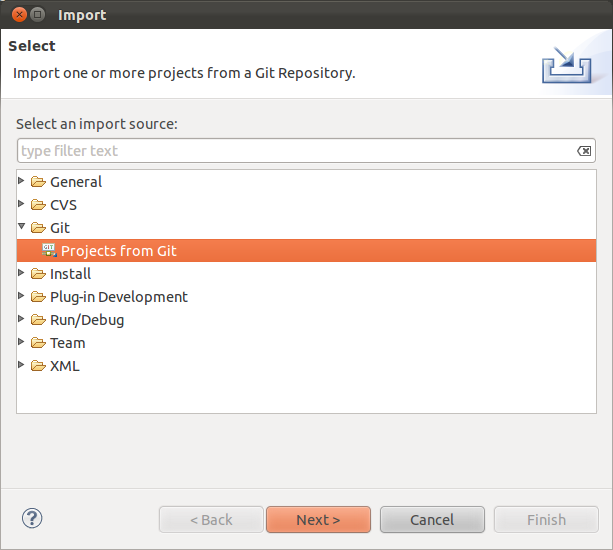
Select Clone URI in the next dialog.
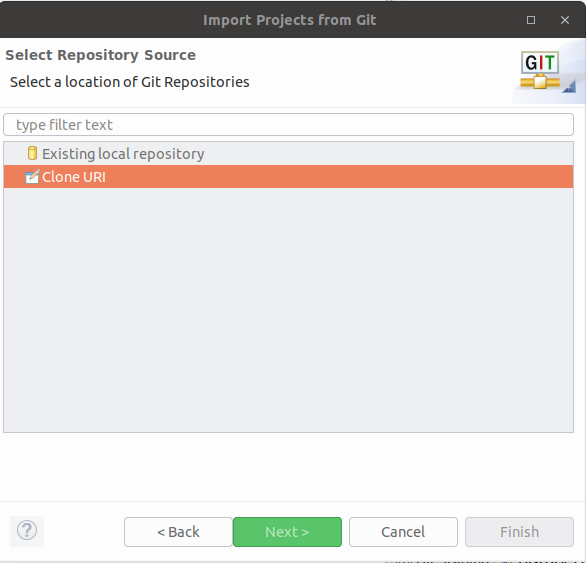
Enter the URL to your Git repository which you desire to clone. You can use the following example URI.
git://github.com/vogella/eclipse4book.git
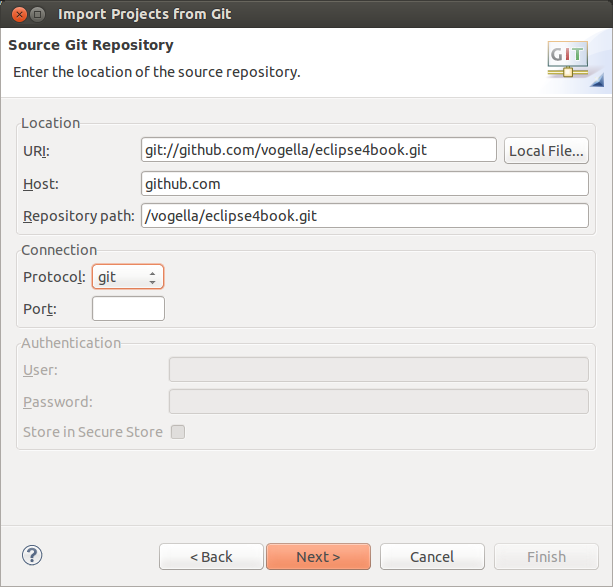
| Git supports several protocols, eastward.g. git://, ssh:// and https://. Yous tin paste the clone URL to the first line of the dialog, the rest of the dialog is filled based on this data. Some proxy servers block the git:// and ssh:// prThe above link uses the git protocol, alternatively you tin also apply the http protocol: http://github.com/vogella/eclipse4book.gitotocols. If you face issues, delight try to use the https:// or http:// protocol. |
Afterwards pressing the Next button the system volition allow yous to import the existing branches. Select at least the primary branch.
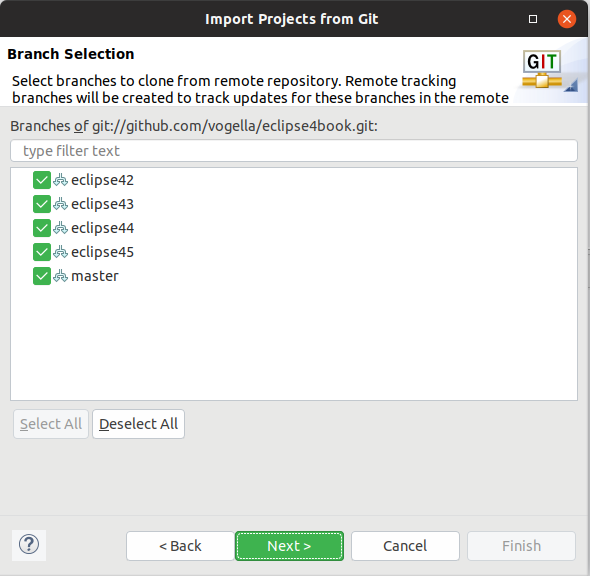
The side by side dialog allows you to specify where the repository should be copied to and which local branch should exist created initially.
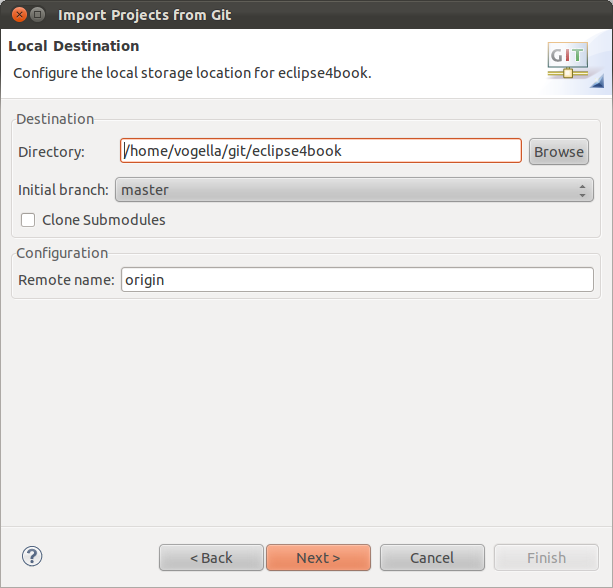
After the Git repository is cloned, you can import existing projects.
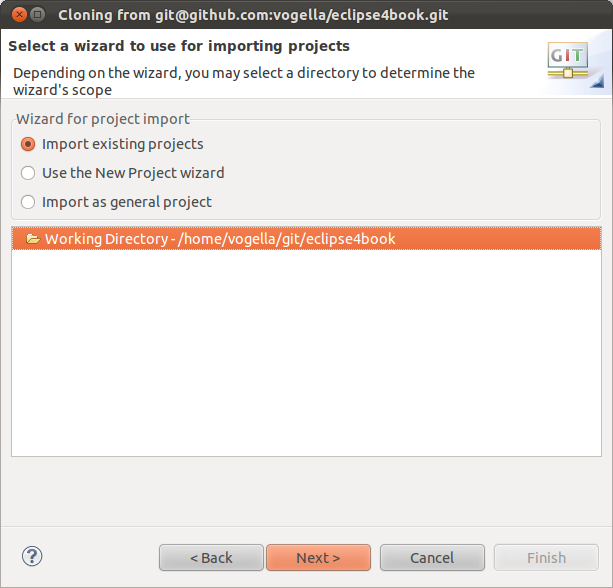
Once this dialog is completed, you have clone the remote repository into a local Git repository. You tin use Git operation on these projects.
| The project may not compile, as you may miss pre-requisites. For this exercises, this can be ignored, the purpose of it was to learn how to clone a repository. |
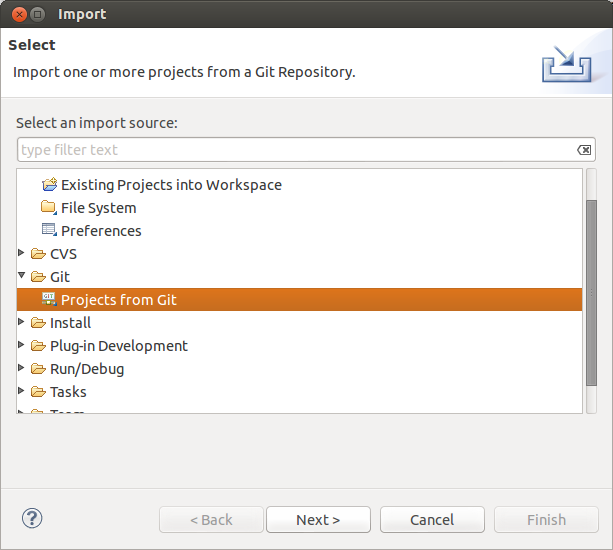
6. Exercise: Import projects from an existing repository
If yous accept already an existing Git repository you tin can add it to the Git Repostory view. After you tin can import the projects into your workspace via the menu entry.
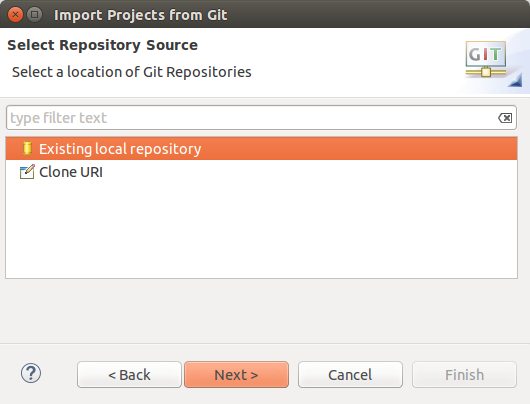
Select Local if you lot desire to important from a local repository or Clone URL if y'all starting time desire to clone the repository.
The following screenshot shows multiple local repositories. To import the projection independent in one of them, select one entries and press the Next button. To add a new local repository to this dialog (and the Git repositories view) apply the Add together… push button.
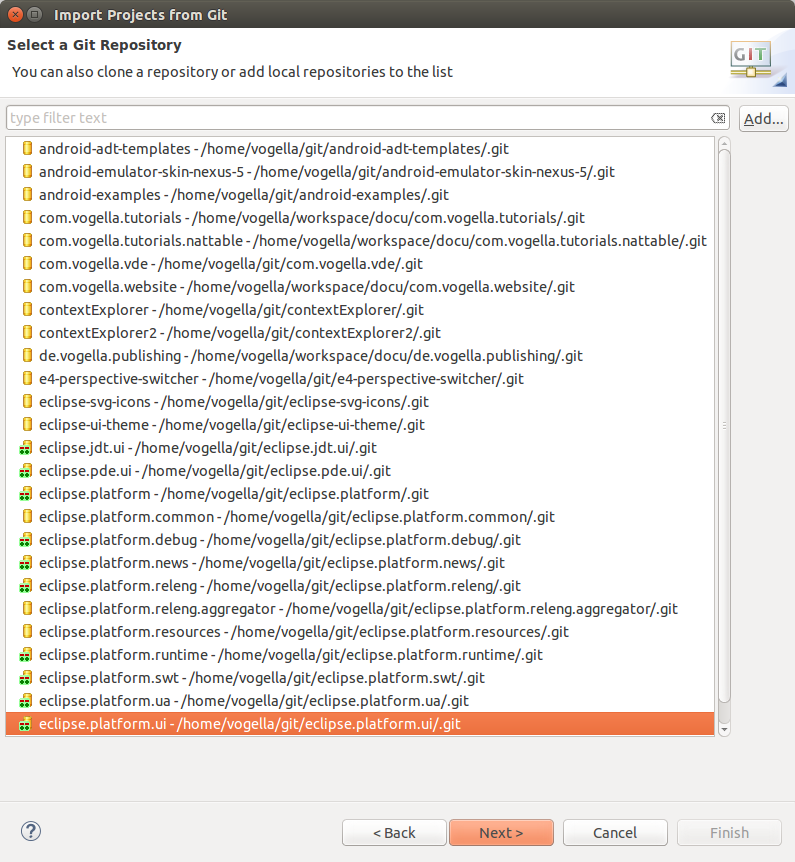
The wizard allows you to specify the projects to import. Later the import the Eclipse IDE is aware that these projects are function of a Git repository.
vii. Exercise: Using interactive rebase in Eclipse
Git allows to adjust the local commit history via the interactive rebase functionality. Eclipse provides support for simplified versions of this equally well every bit support for full interactive rebase operations. This includes irresolute the social club of commits or combining, removing and adjusting commits.
seven.1. Simple interactive rebase operations available via the History view
To reword a commit, right-click on it in the History view and select to modify the commit message.
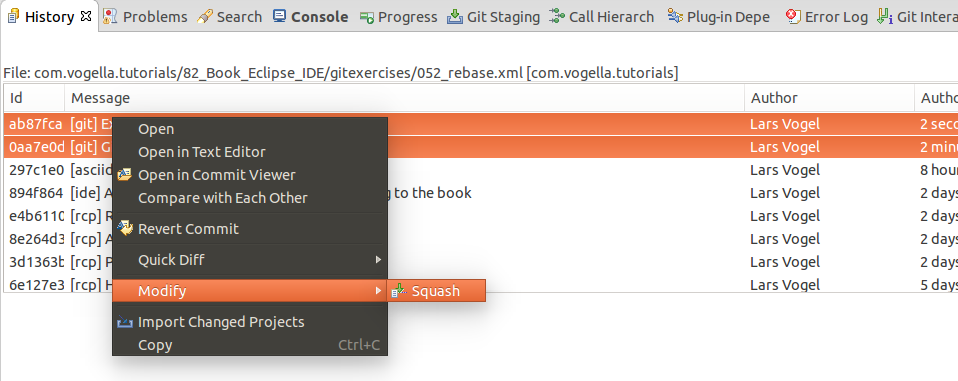
You can squash several commits by selecting them in the History view. Select afterwards the menu entry from the context carte.
The above options are simplified ways to practise an interactive rebase.
seven.2. Performing a total interactive rebase via Eclipse
To start the total interactive rebase open the History view and click on the context bill of fare. Select the last commit preceding the oldest commit yous want to rewrite. Oftentimes this is the one origin/main points to.
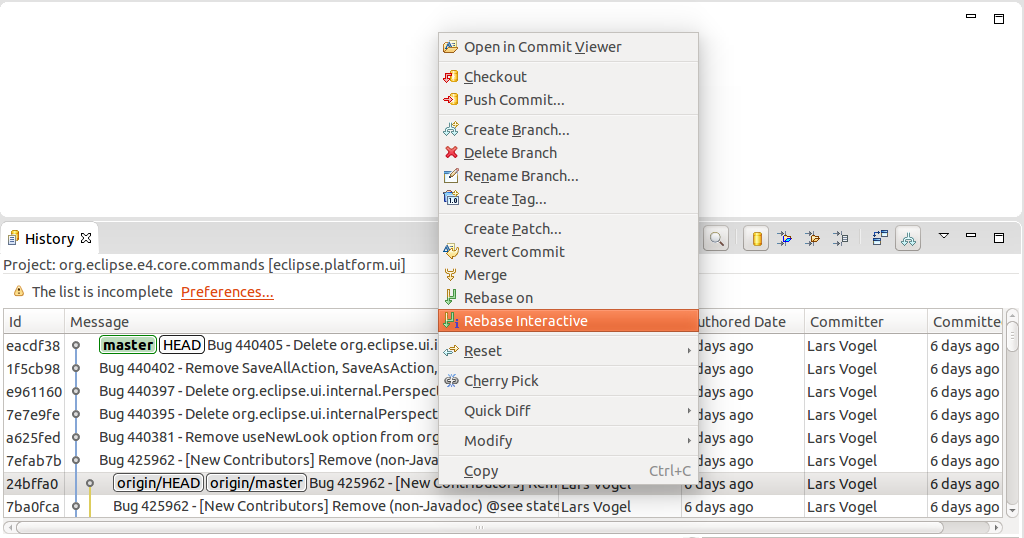
This opens the Git Interactive Rebase view. The Git Interactive Rebase view allow you lot perform the full interactive rebase functionality.
It shows the rebase plan populated with the commits to exist modified. They are sorted in topological order of the sequence in which they will exist processed. This order is the reverse gild which you come across via the git log command or in the History view. The initial activity for all commits is "Pick".
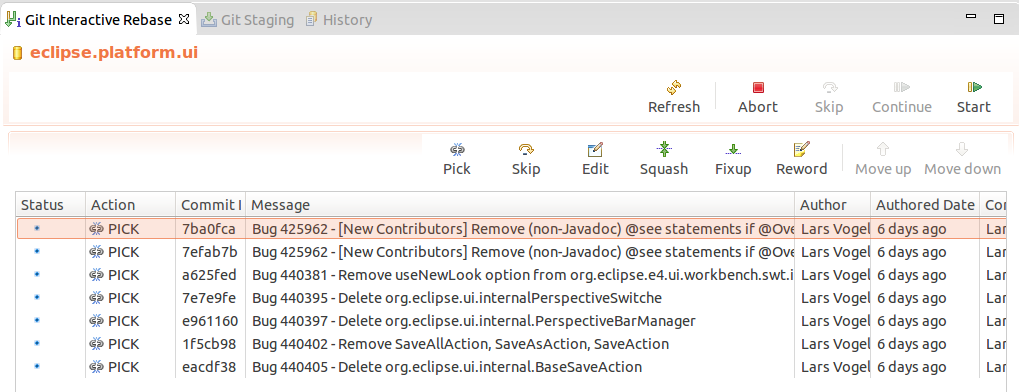
The following deportment are bachelor.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| pick | includes the selected commit, moving pick entries enables reordering of commits |
| skip | removes a commit |
| edit | amends the commit |
| squash | combines the changes of the commit with the previous commit and combines their commit letters |
| fixup | squashes the changes of a commit into the previous commit discarding the squashed commit's message |
| reword | similar to pick but allows modifying the commit message |
Apply this view to finalize the rebase plan. For example, yous can reorder commits with the arrow buttons and select the rebase activeness you desire to utilize to the commit. The following screenshot demonstrates a possible selection.
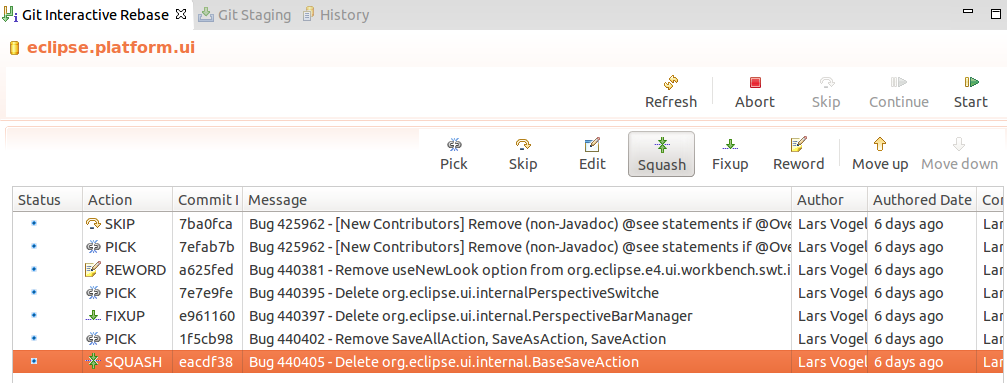
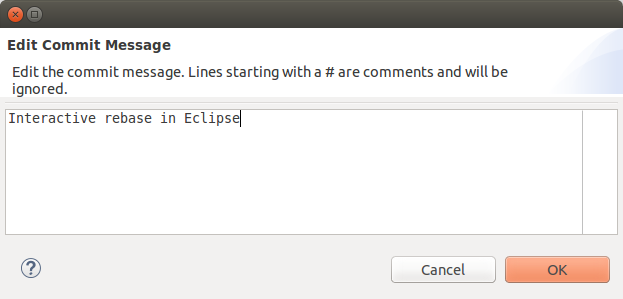
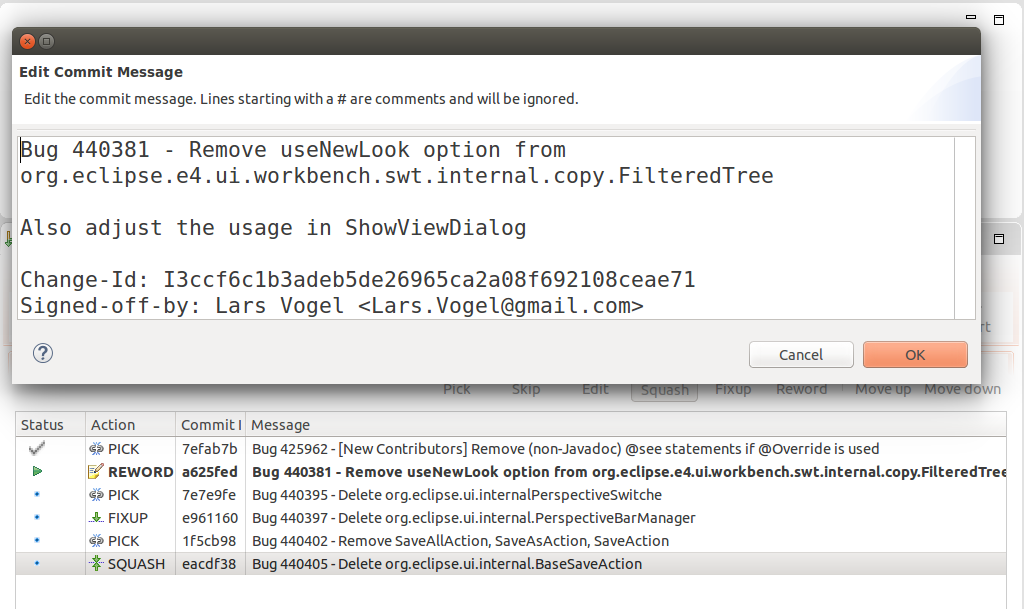
When the rebase plan is finalized, click the Start button to start the interactive rebase command. Eclipse Git processes the plan. Information technology stops at all commits with an activeness which needs user feedback. For example, the reword action which requires inbound the new commit message. The dialog for irresolute the commit message is depicted in the following screenshot.
Here is the result of the rebase operation displayed in the History view.
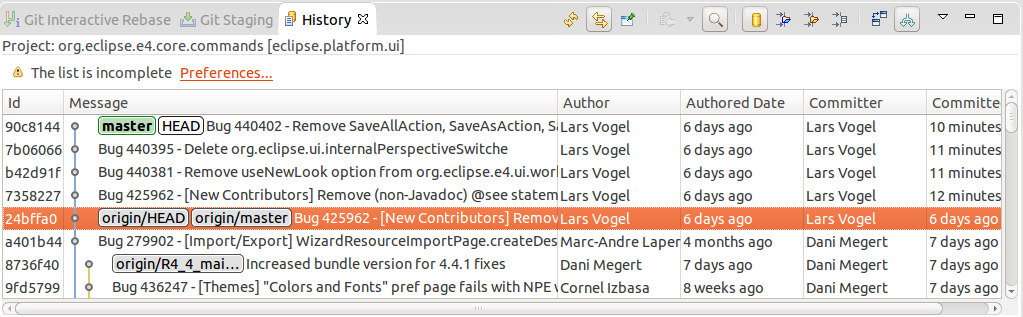
| If something goes wrong during the rebase functioning, you can select Abort in order to end the rebase functioning and roll back to the starting point. |
8. Eclipse Git configuration
The Eclipse IDE uses the default Git settings, eastward.g. done via the command line tooling. You can likewise use the Eclipse IDE to configure these options.
8.1. Git user settings in Eclipse
To utilize Git y'all must configure your full name and email address. This data is used to fill the author and committer data of commits you create. These Git configuration settings can be adjusted via the Eclipse preference setting. Select to see the electric current configuration and to change it.
8.2. Default clone location
If you clone a new repository via the Eclipse IDE, it will be cloned by default to a new sub-folder in a default directory. This default path can be configured via the entry in the Default Repository folder field.
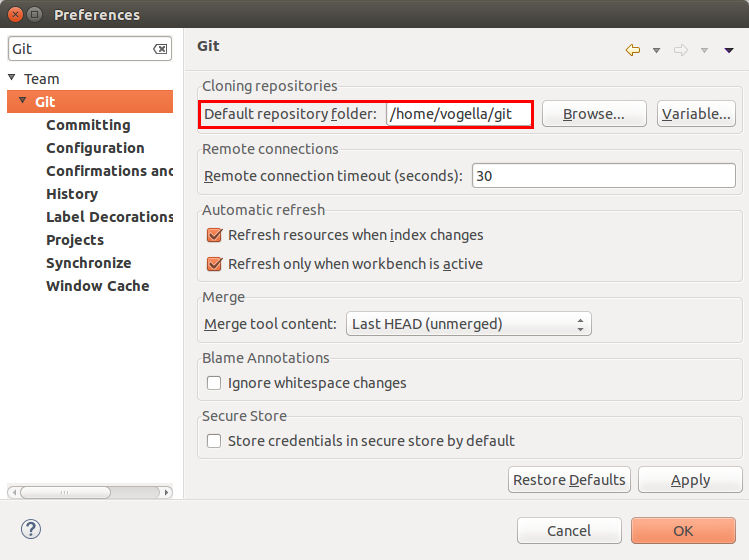
| Y'all tin also use Eclipse configuration variables to ascertain the path, eastward.g., if you want to store repositories in the folder "git" under the Eclipse workspace you may use ${workspace_loc}/git. |
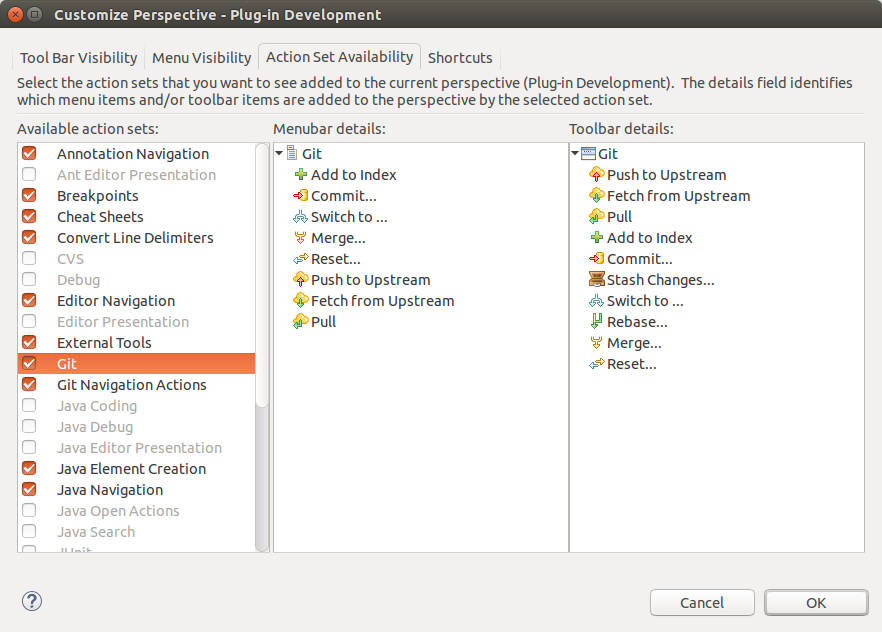
viii.3. Configuring the toolbar and the menu for Git usage
To simplify admission to the common Git operations yous tin can activate the Git toolbar. For this select and check the Git and Git Navigation Actions entries in the Action Prepare Availability tab.
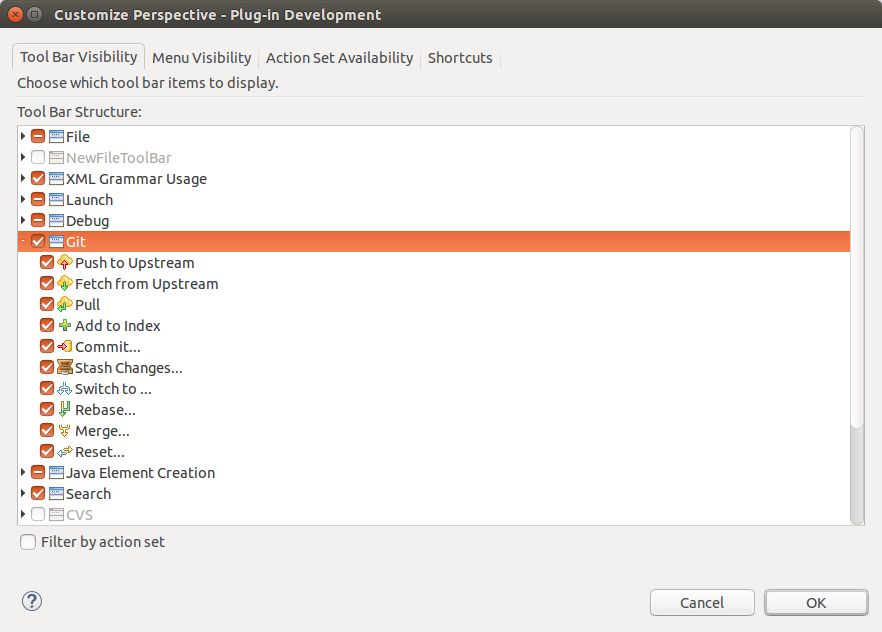
Later you can configure which Git operations should be available via the Tool Bar Visibility or the Menu Visibility tab.
viii.4. Eclipse support for SSH based authentication
You tin create an SSH key pair in Eclipse for SSH based communication. This tin can exist done via .
ix. Details on the Git views
9.ane. Using the Git Repositories view
The Git Repositories view allows you to scan, add. initialize or clone repositories. It also allows to import projects, manage your branches and much more. Yous can open this view via
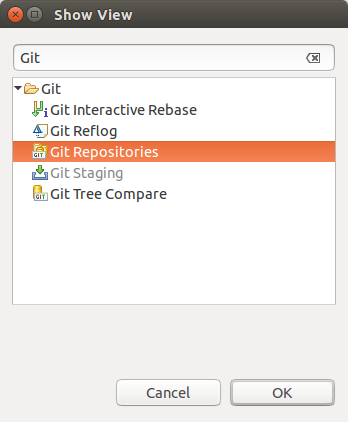
The toolbar allow you to:
-
add an existing local repository to the view
-
clone a repository
-
create a new repository

The content area of the Git Repositories view shows the existing Git repositories and the important information of each repository. The following screenshot shows an example entry.

A right-click (context bill of fare) on an element in the Git repositories view allows yous to perform related Git operations. For example, if you lot right-click on a branch you tin can checkout the co-operative or delete it.
ix.two. Using the Git Staging view
The Git Staging view allows staging and committing as well as reverting changes.
This view presents which files you accept touched and which files will be included in the next commit. Unstaged Changes lists those changes which y'all take done locally but which you take not nonetheless added to the staging area. Staged Changes list those changes which you already have added to the staging area. You lot tin elevate and driblet files from one area to the other. To commit the staged changes you write your commit message and press the Commit push which is highlighted in the following screenshot.

You lot can switch between dissimilar repositories or even restart Eclipse without losing a commit bulletin and information technology allows incremental staging for changes.
You can open the Git Staging view via the menu.
ix.3. Git integration into the Package and the Project Explorer
The Bundle Explorer view shows indicators on the files to show their condition. The most important icon decorators are depicted in the following screenshot.
![]()
The file name describes the state of the file from the following table:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| tracked | File is committed to the Git repository and has not changed. |
| untracked | File is neither staged nor committed. |
| ignored | File is flagged to be ignored by Git operations. |
| dirty | File has changed since the last commit. |
| staged | Changes in the file will be included in the next commit. |
| partially-staged | The resource has changes which are added to the index and additional unstaged changes in the working tree |
| added | Staged but not yet committed, i.eastward. snapshot of this file has been stored in the git database. This condition is the aforementioned as the staged condition, only the file wasn't under Git version control earlier. |
| removed | The resources is staged for removal from the Git repository. |
| conflict | A merge conflict exists for the file. |
A combination of the staged and dingy condition means: some parts of the changed file have been staged while some are nevertheless unstaged. This tin can happen if you stage a file and then once more modify the file before creating the next commit. Yous tin can also alter the staged parts using the compare editor opened by double clicking files in the staging view.
On a project level the explorer view adds the information which Git repository is used to the project name. It as well adds the number of commits that are dissimilar betwixt local and remote tracking co-operative. This way you tin quickly see if your local branch is ahead or behind the remote co-operative it is tracking.
![]()
9.4. Using the History view for viewing the Git history
ix.4.1. Purpose of the history view
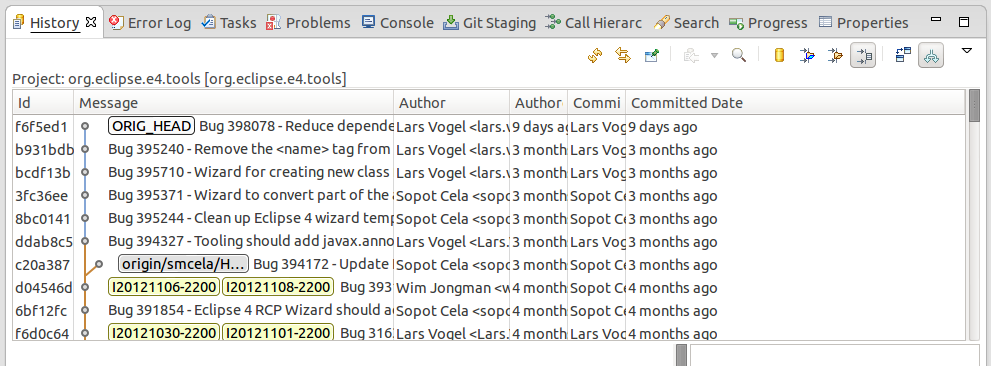
The History view allows y'all to analyze the history of your Git repository and to see to which commits the branches and tags points. This view displays author, date, commit message and the modified files of a commits.
This view is depicted in the following screenshot.
You can open this view via . Alternatively you can open it via the repository node in the Git Repositories view. For this click on the entry. Some views, e.g., in the Java EE-Perspective, do non take this shortcut, in this case use .
To see the history of a resources, select your project, a file or a folder, right-click on information technology and select the Testify in> History context menu entry. Alternative you tin use the Alt+Shift+W shortcut and select the History entry.
You can also configure the History view to display the history of the current choice. Select the highlighted button in the post-obit screenshot for that.

If y'all select a commit yous see the commit message and the involved files.
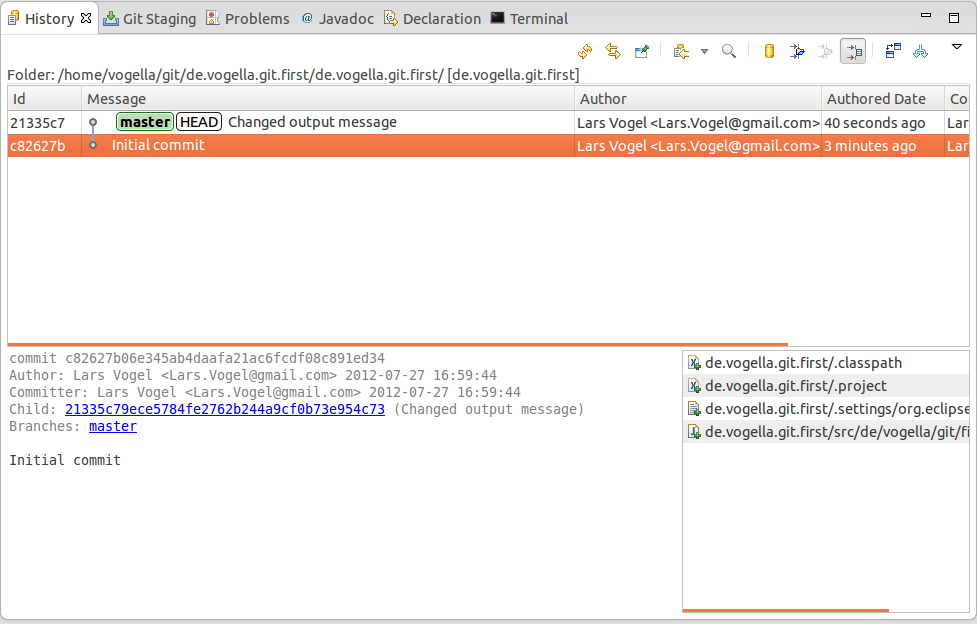
Via right-click on an individual file you can compare this file with its ancestor (the commit before that) or with the current version in the workspace.
| If the "compare mode" toggle is selected from the view bill of fare of the History view you can as well double click a file to compare it to the previous version. |
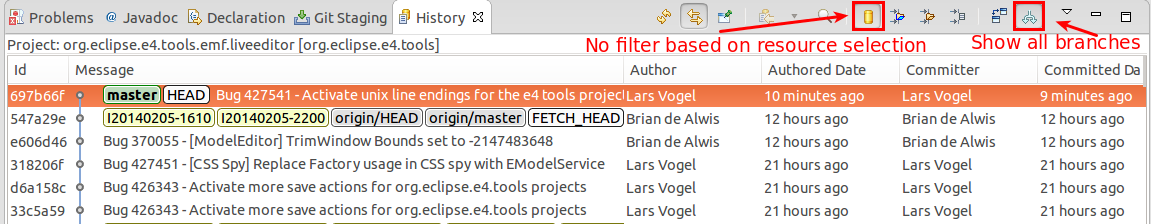
9.4.2. The History view filters
The History view has quite some options to configure which commits are displayed. Its toolbar allows you to customize which commits are displayed. Past default, the History view filters the history based on the current selection and shows merely the agile branch.
If you lot work with several branches, eastward.g., because yous are using Gerrit for code reviews, you lot typically want to see all branch data and remove the filter based on the resource.
The History view allows you to filter based on resources. See the tooltips of the toolbar for the pregnant of the unlike filter options. In order to run across all commits click the highlighted buttons with the Show all changes in this repository and Show all branches and tags tooltips.
The following listing gives an overview of the purpose of the unlike buttons.
Depending on your utilise case you may want to select the following option:
-
prove only those commits which are reachable from the current branch. Hibernate all commits on other topic branches.
-
come across only those commits which changed the selected resource (file, project, subfolder) or information technology's children. East.thousand. display but those commits which touched the selected java file. The electric current selection is shown in the peak right corner of the History view.
-
see only those commits which inverse anything in the parent binder of the selected resources (file, project, subfolder) or information technology's children. E.g. display only those commits which changed the same packet as the selected coffee source.
-
run into only those commits which inverse annihilation in the same project equally the selected resource or it's children. Used when yous are working in a repository which contains multiple projects.
-
don't filter at all. Show all commits of the current repository
The options b., c. and d. are tied to the currently selected resources. Push g. allows that the history view automatically updates when you change the selection.
| If y'all got lost with the different filters and the history doesn't show what you look, set it back to prove everything. Therefore make sure that Show all branches and tags (a) is turned on and Testify all changes in repository (east) is selected. |
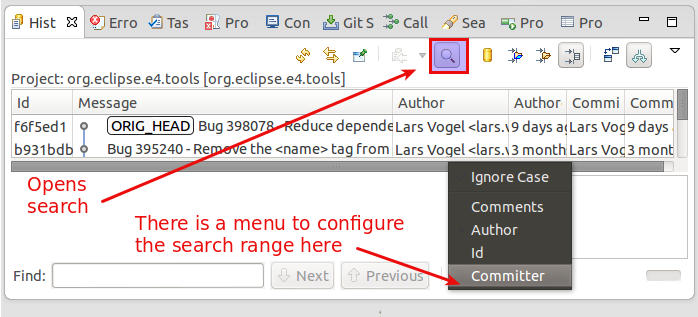
9.4.3. Using search
You can as well search for commits based on committer, writer, ID or comment. For this turn on the Evidence Find toolbar (f) and type in a search string in the Detect field. The commits plumbing fixtures to your search are highlighted. You can combine this search with the filters explained above.
| The Git Search bachelor in the menu is much more powerful and consumes less memory since it doesn't need to also brandish the history. |
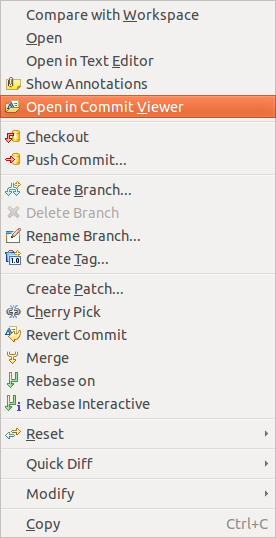
9.four.4. Showing details of a commit
If y'all want to see more than details about a commit, correct-click information technology and select the Open in Commit Viewer entry.
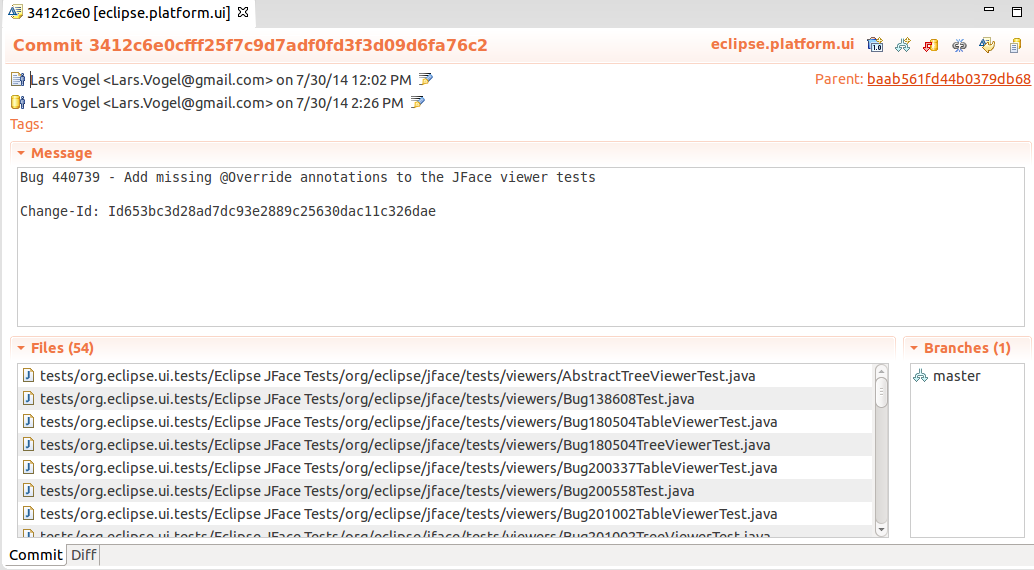
9.5. Commit Viewer
The Eclipse IDE allows to view the content of a commit. For instance,if yous are in the Git repositories view you can open a commit via the main Eclipse carte du jour. To practice this select the menu entry.
If you lot open up a commit you lot can create a tag or co-operative from information technology. You can also revert it, cherry pick it or check it out. You lot can likewise reveal information technology in the history view.
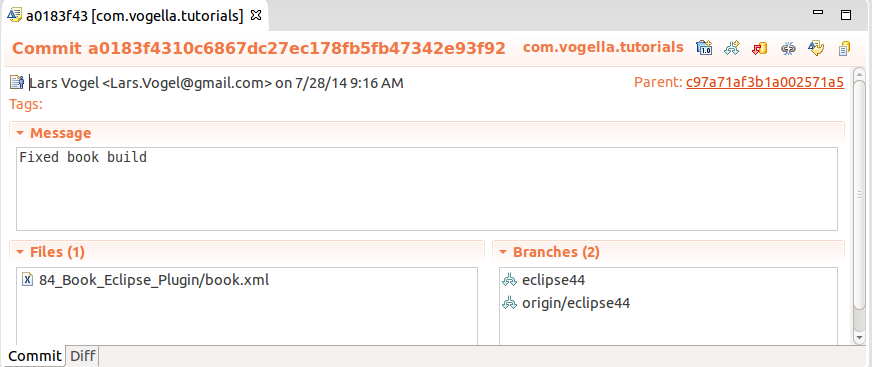
10. Performing Git operations in Eclipse
10.1. Pull, push and fetch
You can use the Git Repositories view to pull, push and fetch to remote repositories. Right click on your repository and select the appropriated operation.
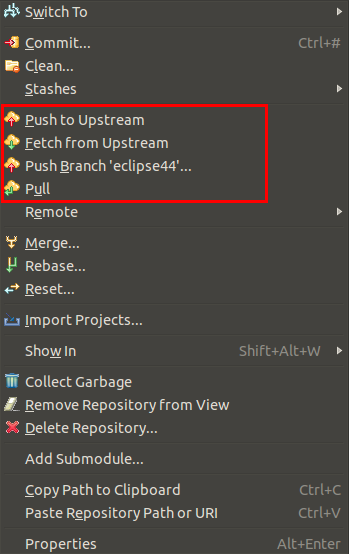
10.2. Basic team operations
One time yous have placed a project under version control you can first using squad operations on your project. The team operations are available via correct-click on your projection or file.
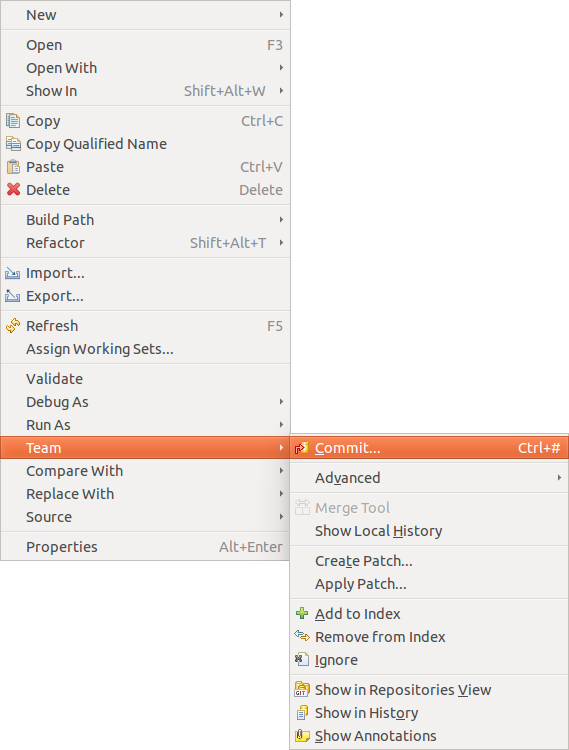
| The Team carte is besides available from the context carte du jour of an opened editor. |
The most important operations are described in the following listing. Select:
-
, to add the selected resource(southward) to the Git index
-
, to open the commit dialog to create a new commit
-
, to create a patch
-
, to apply a patch to your file system
-
, to add together a file to the .gitignore file
-
, to brandish the history of the selected resources(s)
10.3. Team operations available on the project
If you select a project yous can utilise additional team operations from the context menu.
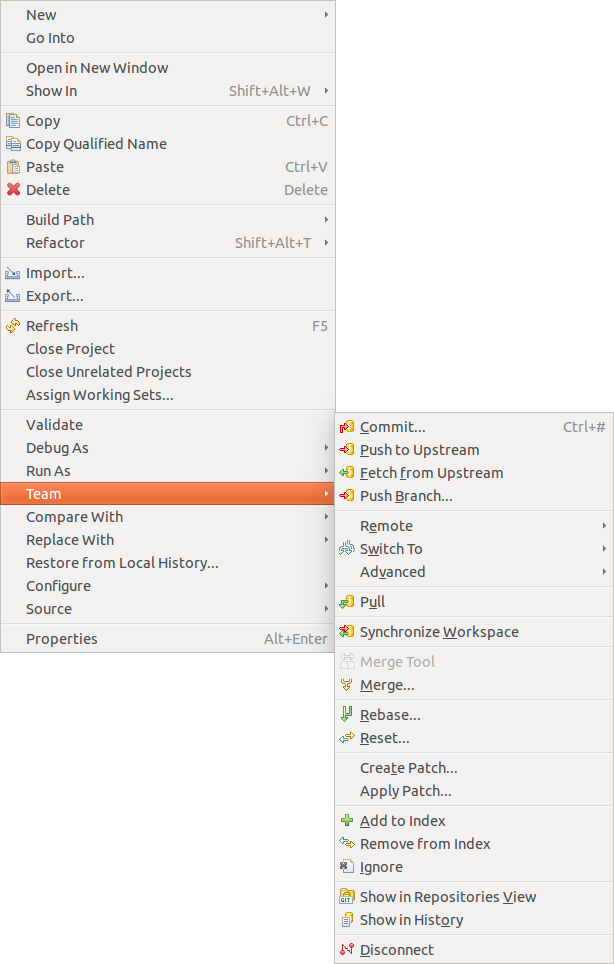
-
to pull in changes from your remote Git repository
-
to fetch the electric current state from the remote repository
-
to checkout existing or create new branches
-
to push button changes to your remote Git repository
-
to create and manage tags.
x.4. Amending a commit
Git amend allows adjusting the last commit. For example you can alter the commit message or add another modification.
The Git Staging view allows y'all to perform the Git amend command via the highlighted button in the following screenshot.
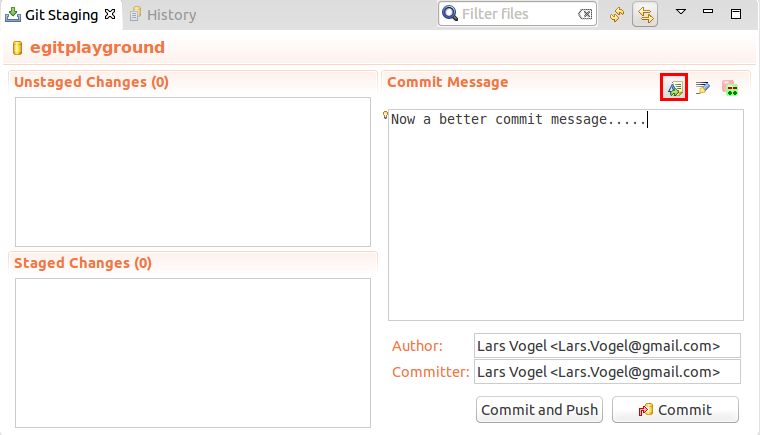
10.5. Creating and switching branches in Eclipse
Right-click your project and select to create new branches or to switch between existing branches.
You lot can likewise switch branches in the History view or the Git repositories view.
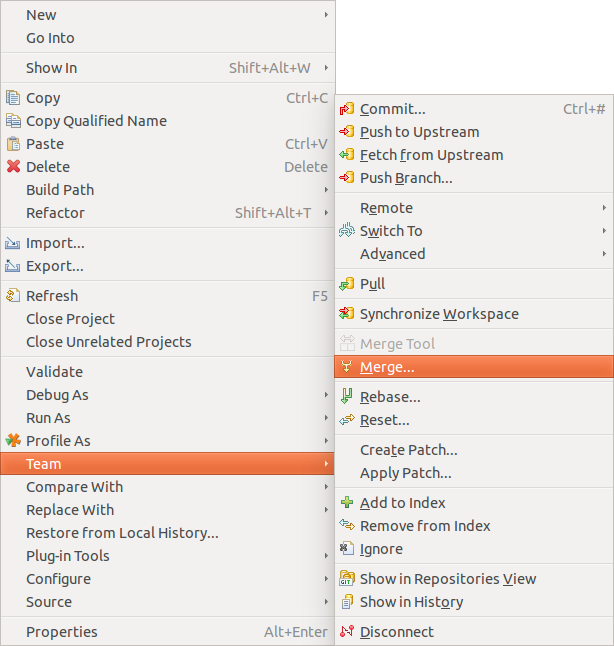
10.6. Starting a merge operation in Eclipse
Eclipse supports merging of branches to add the changes committed on ane branch into another branch.
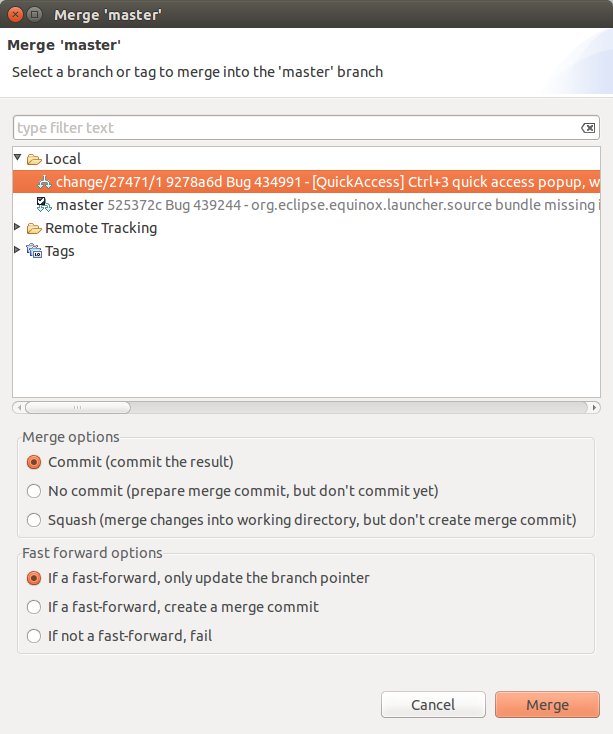
Checkout the branch into which you desire to merge the changes into and select your projection and to offset the merge dialog.
10.7. Rebasing a branch onto another branch
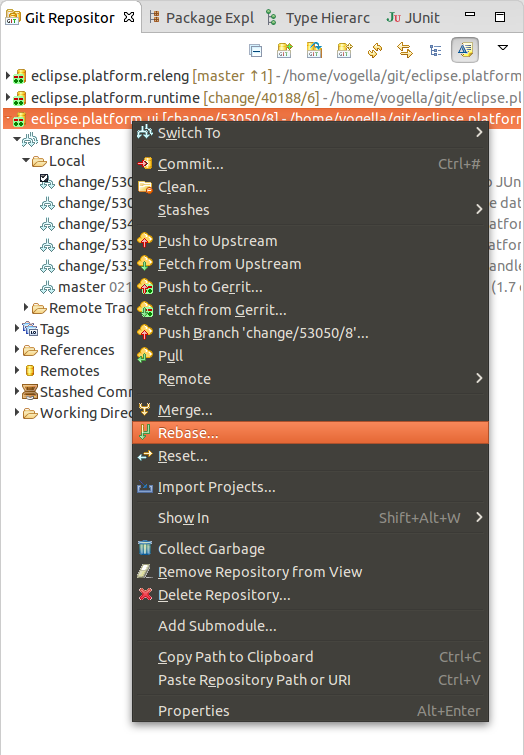
The Git Repositories view allows you to rebase your currently checkout branch onto another co-operative.
Right-click on a repository node and select every bit depicted in the post-obit screenshot.
In the post-obit dialog you can select the branch onto which you lot want to rebase.
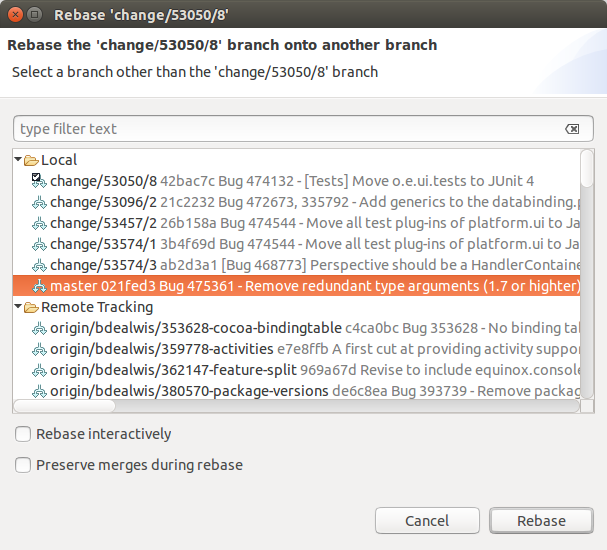
| Y'all tin can as well select the branch to rebase onto from the Branches node of the tree direct. |
If the rebase was successful a dialog is shown. You take to resolve rebase conflicts if they occur. After resolving them, select .
If you want to skip the alien commit and continue with the rebase operation use .
To cancel the rebase operation select .
10.eight. Solving conflicts created by merge, rebase or other operations
If during a Git functioning, ii changes are alien, you have to solve these conflicts manually. Eclipse highlights the affected files in the Package Explorer and Projection Explorer view.
Eclipse Git supports the resolution of these merge conflicts.
To trigger this via the explorer views, right-click on a file with merge conflicts and select .
Yous can too use the Git staging view to detect the alien files. In big projects this is usually faster than navigating the Package Explorer or Project Explorer view.
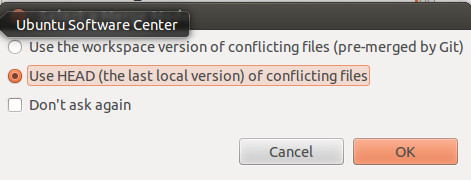
This opens a dialog, asking yous which merge style yous would similar to use. The easiest way to come across the alien changes is to use the Employ HEAD (the concluding local version) of conflicting files as merge style. This fashion you see the original changes on the left side and the conflicting and non-conflicting changes on the right side.
You lot can manually edit the text on the left side or use the Copy current change from right to left button to copy the changes from right to left.
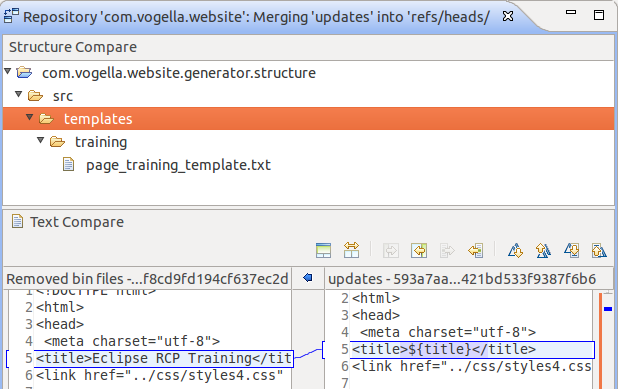
Eclipse likewise allows to show the common ancestor of both commits to make the merge easier. Press the Hide/Bear witness Ancestor Pane push button for that. This is demonstrated past the following screenshots.
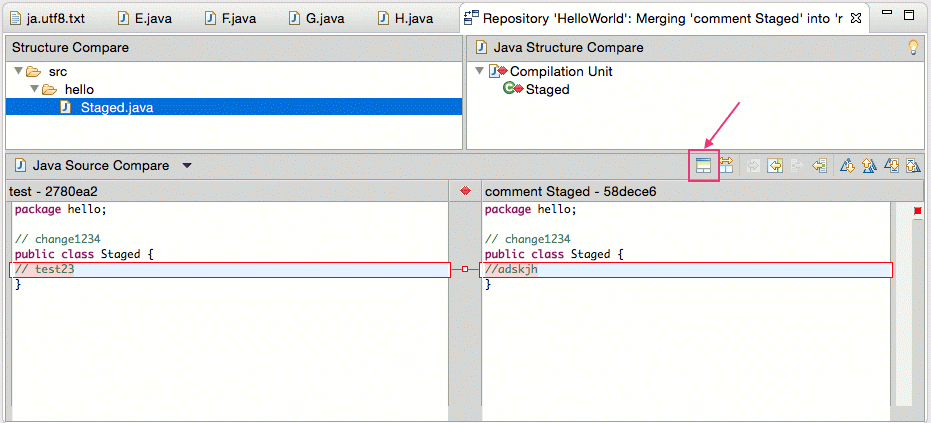
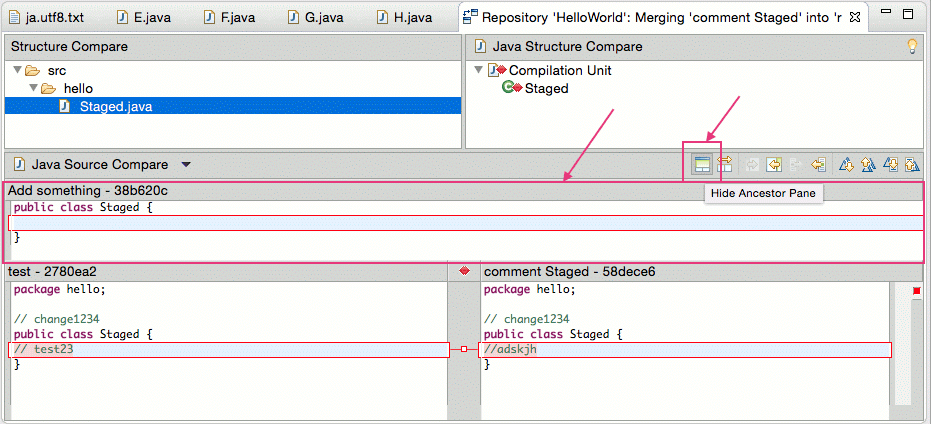
One time you have manually merged the changes, select from the context menu of the resource to mark the conflicts as resolved and commit the merge commit via .
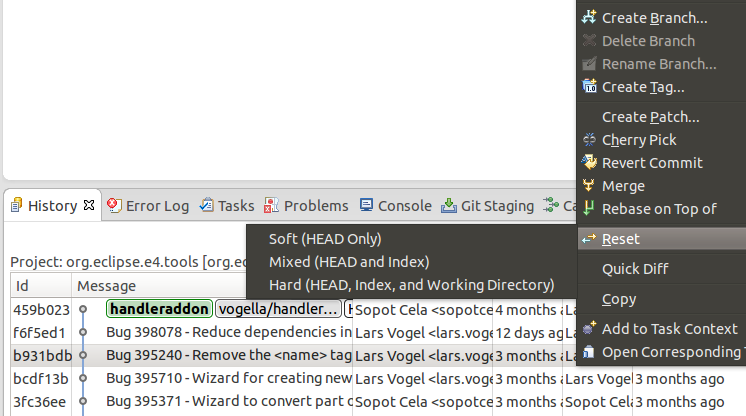
x.9. Git reset and Git reflog
The History view allows you to reset your current branch to a commit. Correct-click on a certain commit and select and the reset way you lot would like to use.
ten.10. Finding "invisible" commits with the Reflog view
Commits are not visible in the Git history if they tin can't be reached from a branch or tag. This might happen during a reset, commit better or rebase operation. By default, such invisible commits are removed afterwards two weeks by the Git system.
The Git Reflog view keeps track of the movements of the Caput pointer and the movements of each branch. This view allows you to find a commit once more, e.g., if you used the git reset --hard control to remove certain commits.
ten.11. Selecting individual commits via git cherry-option
In the History view, you tin can cherry-pick a commit via the context menu. Cherry-pick allows to move selected changes describes by a commit to some other branch. You tin can also use information technology in combination with a Git reset to perform a simplified interactive rebase.
Lets assume the post-obit situation, in which y'all would like to remove the "Bad commit" from the history described by the master branch.
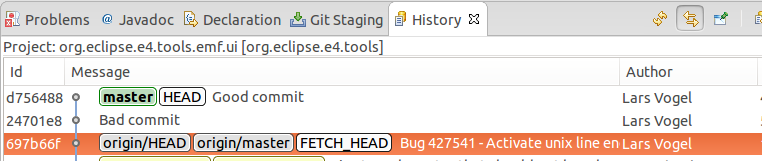
You could outset with a hard reset of the branch to origin/master. This will move the principal branch pointer to the commit described by origin/master. The Good and the bad commit are not reachable anymore past the master co-operative.
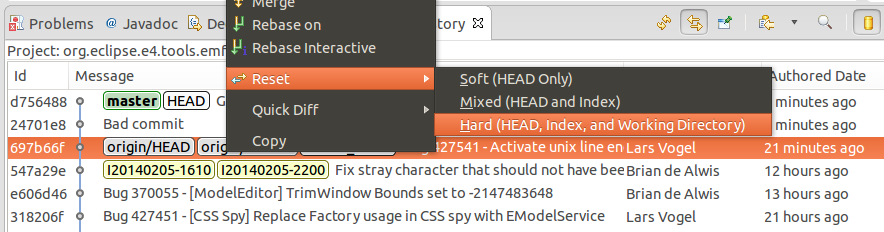
To re-utilize the changes past the "Good commit", ruby-pick the skillful commit.
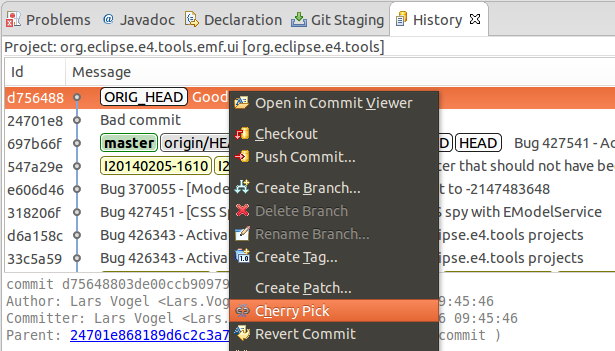
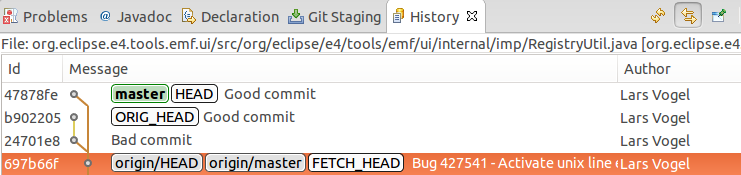
This results in a history without the bad commit.
10.12. Comparison and replacing files based on the Git history
10.12.one. Comparing files
Eclipse Git allows you lot to compare a selected file, folder or projection with another commit or with the Git index. Use to open the card. Afterwards select with what you desire to compare. The Caput Revision option is depicted in the following screenshot.
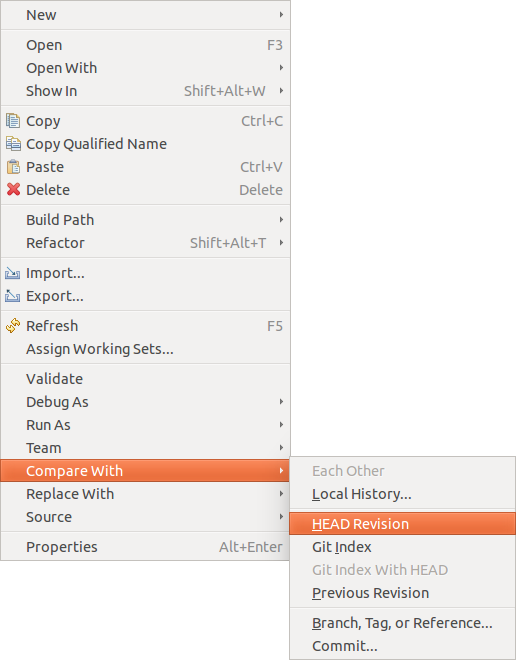
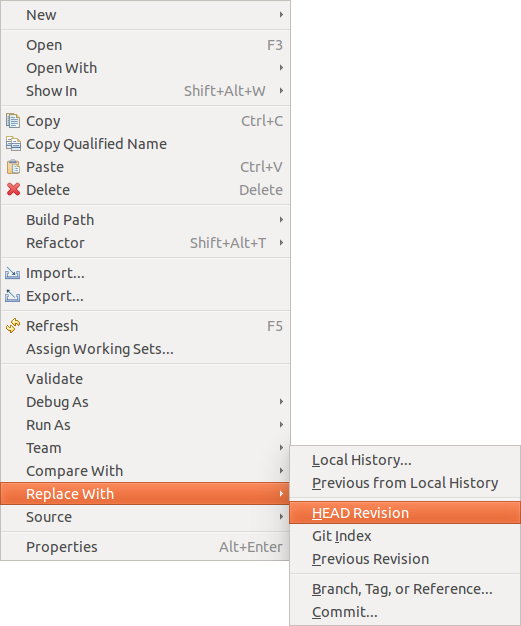
10.12.2. Replacing files
The carte entry allows you to supplant the current selection with the version contained in the selected commit or the Git index.
11. Meet Git information line by line (aka git blame)
Eclipse allows to brandish the information which commit and person alter a line. To enable this, right-click on your file and select .
| This action is likewise available via the line ruler in about editors. |
Later on, you can identify the mouse on the left side of the editor. A popup dialog shows the commit data and the change applied by the shown commit.
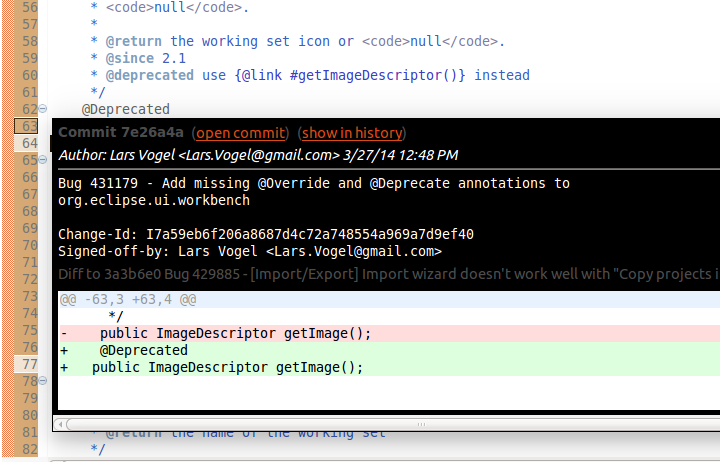
| To ignore whitespace changes in the Git blame annotations in Eclipse, select and select Ignore whitespace changes. |
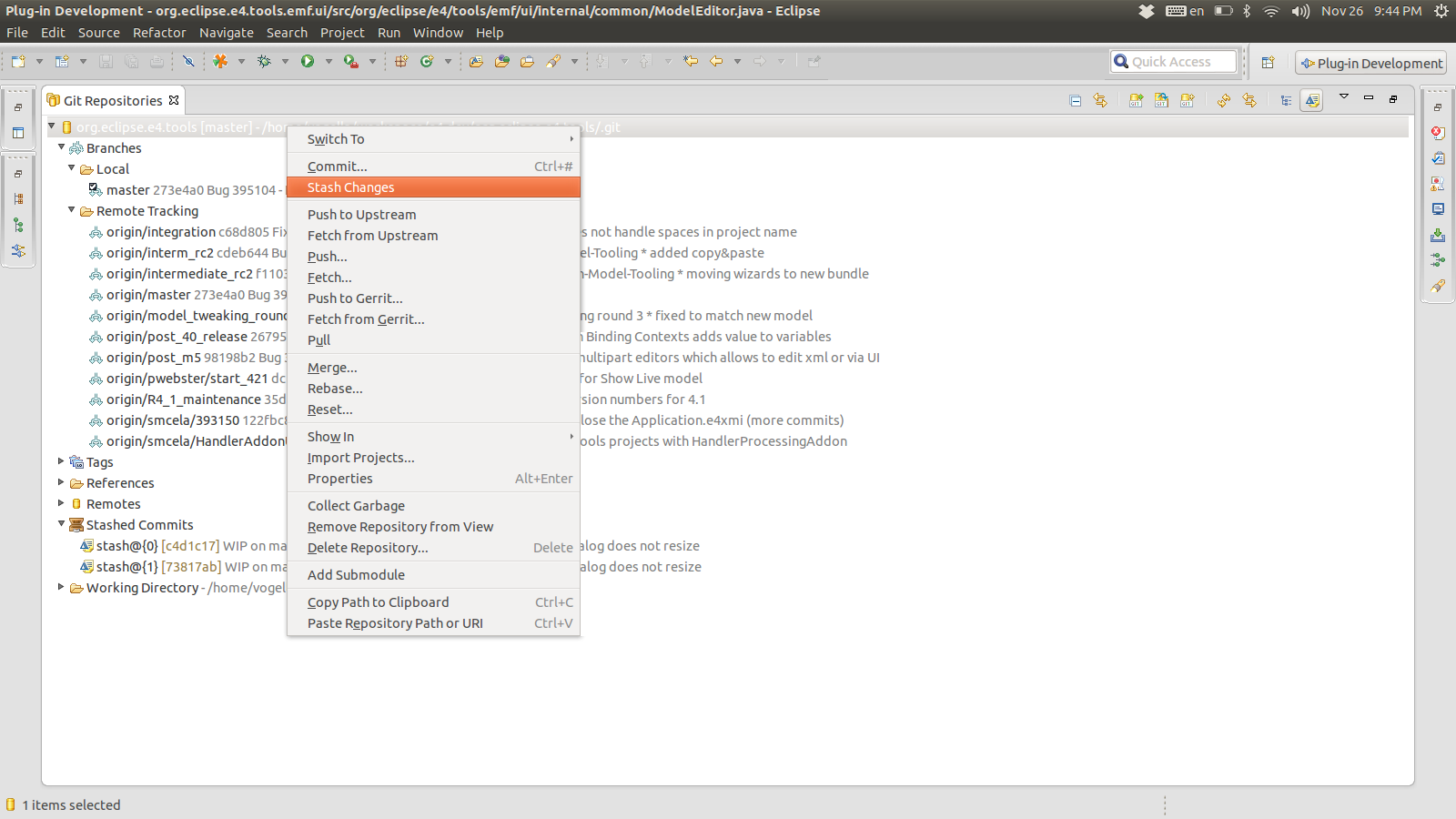
xi.1. Stash via the Git repository view
The git stash command is available in the Git repositories view. Correct-click on your Git repository and select Stash Changes.
11.2. Creating patches
To create a patch for a prepare of changes with Eclipse, select the resources for which you desire to create a patch in the Package Explorer view. Now, correct click and select .
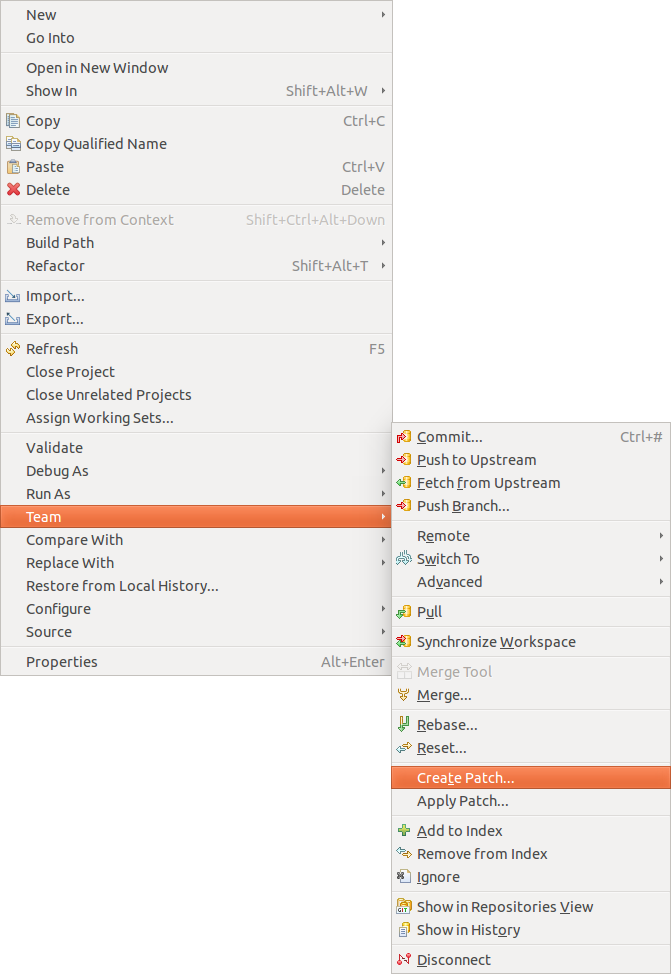
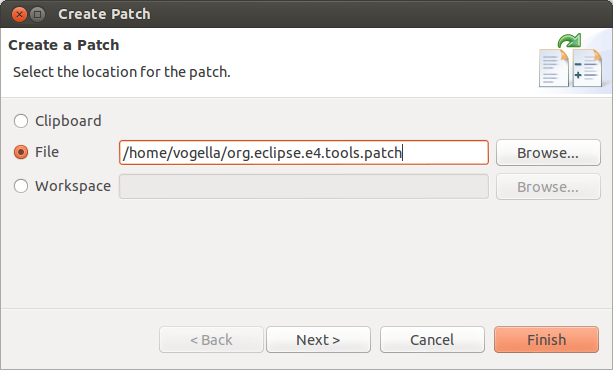
The resulting file can be used to go applied to another Git repository, via . You lot tin also apply the patch on a system where Git isn't installed at all, i.e., yous don't need a Git repository to apply a patch.
12. Using Eclipse Git with GitHub
12.1. Clone project
Re-create the URL from GitHub and select in Eclipse from the menu the
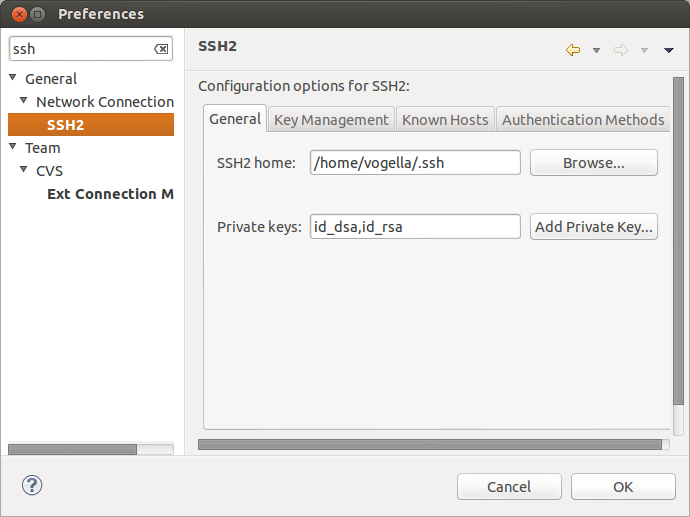
Eclipse fills out almost of the fields based on the URL in the clipboard. Enter your user and password to exist able to push to GitHub. Alternative yous can too use an SSH key. You can configure Eclipse to know your SSH via the preference setting. This setting is depicted in the post-obit screenshot.
12.2. Push button changes
Later you lot made changes and committed them to your local repository, you can select on the project folder, to push your changes to your GitHub. This requires write access to the GitHub repository.
13. Writing good commit letters
thirteen.1. Importance of Git commit messages
A commit adds a new version to the repository. This version is described by a commit message.
The commit message describes the changes recorded in a commit. It should assist the user to understand the history of the repository.
A commit message should therefore be descriptive and informative without repeating the lawmaking changes.
13.two. Guidelines for useful commit messages
A commit message should have a header and a body. The header should be less than 50 with a maximum of 72 characters. The body should wrap its text at 72. The body is separated from the header past an empty line.
This ensures that the commit message is displayed well on the command line or in graphical tools.
The body describes the reason why the change was made. The changes in the file can be reviewed with the aid of Git.
The commit message should be in present tense, e.1000., "Adds better error handling" instead of "Added better error handling".
The terminal paragraph can also contain metadata as central-value pairs. This data is too referred to equally the commit message footer.
This metadata can be used to trigger a certain behavior. For case, the Gerrit code review system uses the Change-Id key followed by a change-id. This changed id is used to identify to which review the message belongs.
The commit message footer can also have e.1000., 'Signed-off-by'. Or it may link to a bug tracking organization, e.g., 'Bug: 1234'.
xiii.3. Example message
The following can serve as an example for a commit message.
Short summary (less than 50 characters) Detailed explanation, if required, line suspension at around 72 characters more stuff to depict... Fixes: problems #8009 Alter-Id: I26b5f96ccb7b2293dc9b7a5cba0760294afba9fd xiii.4. Good and bad example for a Git history
The following listing shows the output of the git log --oneline command of a Git repository with bad commit messages. The get-go value in each line is the shortened SHA-1, the second the commit message. This history is not useful.
21a8456 update 29f4219 update 016c696 update 29bc541 update 740a130 initial commit The next listing shows the history of some other Git repository in which better commit letters take been used. This history already gives a practiced overview most the activities.
7455823 Adds search and filter to the model editor tree 9a84a8a Missing DynamicMenuContribution in child selector 952e014 Fixes spelling mistake in Toolbar/Add together kid 71eeea9 Adds option to import model elements from legacy RCP 123672c New Awarding sorcerer is missing dependencies 97cdb9a Creates an id for handlers The higher up example as well adds the corresponding problems number to the commit message. Some teams (like the Eclipse platform squad) use this approach, others prefer to add the problems number to the commit messages.
14. Contributing to EGit - Getting the source code
This support is provided by the EGit project via a prepare of plug-ins (software component).
Eclipse uses the JGit library to perform the Git commands. JGit is a library which implements the Git functionality in Java.
EGit is hosted on git://git.eclipse.org.
Source: https://www.vogella.com/tutorials/EclipseGit/article.html

0 Response to "How to Upload Code to Github and Share Eclipse"
Post a Comment